E-METHANOL, THE GREEN FUEL POWERING TOMORROW
WHAT IS E-METHANOL?
E-methanol is a renewable liquid fuel produced by synthesizing renewable hydrogen (H₂) with captured carbon dioxide (CO₂). When both inputs originate from sustainable sources—renewable electricity for hydrogen, and CO₂ captured from biogenic or industrial sources—the resulting fuel can significantly reduce lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions. Unlike other e-fuels, eMethanol benefits from mature handling, distribution, and combustion technologies, making it one of the most practical alternatives for decarbonizing sectors where direct electrification is not feasible.
E-methanol is a unique fuel. It combines the stability of biofuels with the scalability of eFuels.
This makes it safe and easy to handle, well suited for the scaling needs of the shipping and aviation sectors, and it can leverage 100Mt of global transport and bunkering infrastructure that has existed for decades.
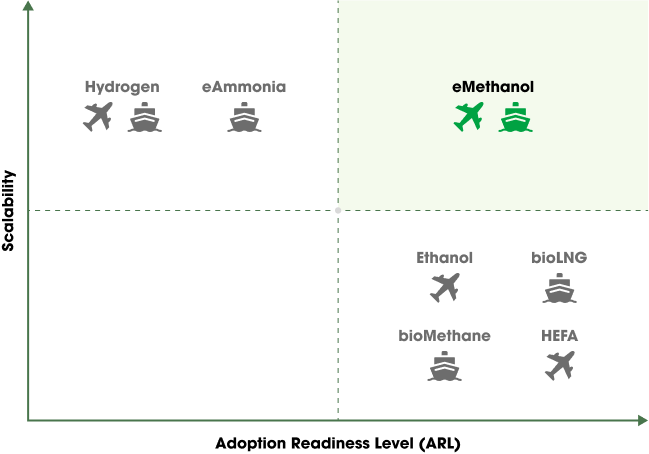
The market potential for this sustainable fuel is enormous.
eMethanol
Fuel for:
Road Transportation
Maritime Shipping
Aviation
Chemical industry
HOW IS E-METHANOL OBTAINED?
E-Methanol is produced through a process that combines renewable hydrogen (H₂) with captured carbon dioxide (CO₂) in a catalytic reaction. This process results in a renewable, carbon-neutral liquid fuel that can replace fossil-based methanol.
The production of eMethanol involves two key steps:
Renewable Hydrogen Production
Renewable hydrogen is generated through electrolysis, where water (H₂O) is split into hydrogen (H₂) and oxygen (O₂) using electricity from renewable sources such as wind or solar power.
eMethanol Synthesis
Carbon dioxide from industrial emissions or directly from the air is then combined with renewable hydrogen in a reactor using a catalytic process to synthesize eMethanol.
E-METHANOL AS A CARBON-NEUTRAL ALTERNATIVE FUEL
The classification of eMethanol as carbon-neutral is based on the use of CO₂ that would otherwise be released into the atmosphere. However, the use of alternative fuels considered carbon-neutral is still subject to emissions accounting throughout the entire process, as stipulated by the relevant regulations. At HyFive, we are deeply committed to complying with these regulations and maximizing the amount of CO₂ emissions avoided by strictly adhering to the applicable standards.
The Role of E-methanol
Global energy demand is projected to increase by up to 30% by 2040, while emissions from hard-to-abate sectors like maritime shipping, aviation, and heavy industry remain major climate challenges. In this context, eMethanol offers a practical decarbonization pathway—particularly for international shipping—thanks to its favorable physical properties, low infrastructure barriers, and compatibility with existing combustion technologies. As regulatory momentum grows (e.g. the IMO Net-Zero Framework), fuels like eMethanol are expected to play a central role in the global effort to reduce industrial emissions and meet long-term climate goals.
Benefits of E-methanol
Compared to other alternative marine fuels such as ammonia, LNG, or hydrogen, eMethanol offers a balanced combination of safety, energy density, and logistical practicality. Its key advantages include:
- Liquid at Ambient Conditions: eMethanol is a liquid at room temperature and pressure, which simplifies storage, transport, and bunkering using existing infrastructure—unlike hydrogen or ammonia which require pressurization or cryogenic temperatures.
- Lower Toxicity and Safer Handling: eMethanol is less toxic and corrosive than ammonia, with a long-established safety protocol in industrial applications and marine operations.
- Proven Technology Readiness Dual-fuel: eMethanol engines are already in commercial use, and retrofitting is technically feasible, reducing time-to-deployment for fleets.
- Lower Infrastructure Costs: Because methanol can be handled using conventional fuel systems (with minor adaptations), it avoids the high capital costs associated with LNG or ammonia storage and refueling infrastructure.
- Regulatory Alignment: eMethanol aligns with upcoming regulations on fuel carbon intensity (e.g., EU FuelEU Maritime, IMO GHG Strategy), potentially benefiting from carbon pricing and credit schemes.